Masa week 3 ni sir Amir ajar slow je so hm saya bnyk mengantuk maa.. input tu mcm kurang je haha sorry sir 

In week 3, kitorg masuk bab baruu
CHAPTER 2: PRICING THEORY
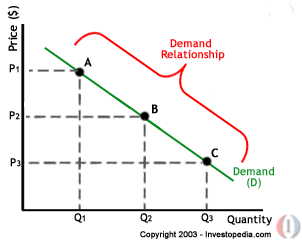
DEMAND
 Price of related goods
Price of related goods Substitute goods
Substitute goods where if P of product A increases, they will change to other product such as product B. If P of product A increases, the Qd for product A decreases (LAW OF DEMAND). Thus, they will look for other altenatives leading Qd for product B increases.
where if P of product A increases, they will change to other product such as product B. If P of product A increases, the Qd for product A decreases (LAW OF DEMAND). Thus, they will look for other altenatives leading Qd for product B increases. Complementary goods
Complementary goods goods are used together with another product. Eg. Car and petrol. If P of car increases, Qd for petrol decreases
goods are used together with another product. Eg. Car and petrol. If P of car increases, Qd for petrol decreases Inferior goods
Inferior goods goods that decreases in demand when income increases. Eg, used cars, salt fish and low grade rice.
goods that decreases in demand when income increases. Eg, used cars, salt fish and low grade rice. Taste and fashions is when the product is fashionable, the demand increases. If product becomes outdated, demand will decreases.
Taste and fashions is when the product is fashionable, the demand increases. If product becomes outdated, demand will decreases. Population is when the Qd of product depends on the population size, If population size is big, then Qd of product increases
Population is when the Qd of product depends on the population size, If population size is big, then Qd of product increases Price expected is when the P of product are going to rise in future, they buy more before the P rises.
Price expected is when the P of product are going to rise in future, they buy more before the P rises.
6. Movement along and shift in the supply curve
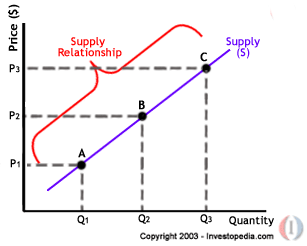
SUPPLY
- Definition of Supply
 The ability and willingness to sell
The ability and willingness to sell - Law of supply
 positive relationship between price of product, P and quantity supplied, Qs. If P increases, then Qs increases.
positive relationship between price of product, P and quantity supplied, Qs. If P increases, then Qs increases.
- Individual supply
 relationship between Qs by single seller and its P
relationship between Qs by single seller and its P - Market supply
 relationship between total Qs by all seller and its P
relationship between total Qs by all seller and its P - Determinant of supply
 Price of related goods
Price of related goods Substitute goods
Substitute goods Supply of product will decrease if there is an increase in the price of substitute product. Eg. Qs of product A will decrease if P of product B increases. When P of product A increases, the Qs of of product A will increase (LAW OF SUPPLY). Thus Qs of product B decreases
Supply of product will decrease if there is an increase in the price of substitute product. Eg. Qs of product A will decrease if P of product B increases. When P of product A increases, the Qs of of product A will increase (LAW OF SUPPLY). Thus Qs of product B decreases Expected future price is when the seller expects the P will increase in future, the current Qs will be decrease (vice versa)
Expected future price is when the seller expects the P will increase in future, the current Qs will be decrease (vice versa)
6. Movement along and shift in the supply curve
Thanks for reading !










0 Comments:
Post a Comment
wanna leave a comment ? yeay ! i love you